What is DNS..? How does it work..?
How does DNS work…?
When we go to www.techenthu.in, we get the website loaded on our browser. How does your computer or browser get the particular webpage only.
Every website has an corresponding IP address. Say, type 129.42.38.1 in your browser, www.ibm.com pops up into your browser.
Every software developer needs to know this basic concept 🙂
What is DNS..?
Domain Name Server is Application layer Protocol used by World Wide Web (WWW). It can be assumed as gigantic address book where website has a corresponding IP address. Just like our names and contact numbers. www.ibm.com has 129.42.38.1 IP address.
How does DNS fetch corresponding IP address…?
Look into 4 layers and will explain it in detail
1. Resolving name server – Configured manually or automatically within our operating system to query IP address for the browser.
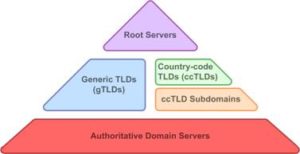
2. Root Server – When we browse www.google.com it actually searches for www.google.com.. Observe the dot after com . But we never see that in the browser. The dot represents Internet’s namespace. There are more than 380 root servers in the world and divided into 13 groups.
3. Top Level Domain Server – Top level domain (TLD) refers to the part that follows immediately after the dot symbol i.e. .com, .org, .net, .in etc.,
4. Authoritative Name Server – Contains IP addresses of a particular Top Level domain from domain’s registrar. Domain registrar is where we purchase the domains.
How it works…?
The browser determines whether it knows what the IP address is, which could be in memory in the Cache. If it doesn’t know, operating system is configured to ask Resolving name server for IP addreses.
The operating system queries resolving name servers, ie www.google.com. The only thing all resolving name servers should know where to find THE ROOT name servers. The root name servers replies with IP address where to find TLD (Top Level Domain) servers.
Now resolving name servers queries TLD servers, which replies with IP addresses to find ANS (Authoritative name servers) using Domain registrar like bigrock, godaddy etc.,
It responds with the actual IP address to the resolving name server, which it stores it in cache and gives it back to the browser.
This process happens in blink of a eye. Once a website’s corresponding address is achieved, the IP address is stored in a cache of resolving name servers of the operating system, just like a phonebook, having website name with corresponding IP address.